Fleet Broadband and BGAN
Overview
FleetBroadband (FBB) and BGAN are satellite-based services providing Internet access and voice services from Inmarsat. There are many different terminals that can be used for each of these two services. Please follow the manufacturer-provided installation instructions for your specific FBB or BGAN terminal.
This guide describes the procedures for cabling and configuring FleetBroadband and BGAN terminals to Lantronix Local Managers.
 |
 |
Target audience
This guide is for trained, qualified network support technicians responsible for installing the FleetBroadband and BGAN terminals in conjunction with the Lantronix Local Manager.
Physical connection
Both FBB and BGAN terminals have an Ethernet interface which is cabled to the Local Manager's GE-1 port. Depending on installation preference, this connection can be made either directly between the Local Manager and terminal or through a LAN switch.
Out of band configuration
The Local Manager must be configured to use its secondary Ethernet interface (GE-1) as its out of band (OOB) path. This can be done either through the Local Manager or the Control Center. Both configuration methods are described below. Local Manager
[admin@LantronixLM]# config system secondary
--- Existing Values ---
Type: bonded
Bonding Link: yes
Primary Ethernet Link: yes (bonded primary)
Auxiliary Ethernet Link: yes (bonded)
Change these? (y/n) [n]: y
--- Enter New Values ---
Type [bonded]: outband
Use DHCP (y/n) [n]: y
speed/duplex [auto]:
DNS Server IP 1:
DNS Server IP 2:
Warning: Remote connections may be lost if you commit changes.
Do you want to commit these changes? (y/n): yThe example above assumes DHCP assignment of an IP address to the Local Manager. If required, a static IP address can be assigned to the Local Manager secondary Ethernet interface. If the BGAN device is address translating (NAT) using an IP address that is not world routable, there are some additional steps that must be taken to allow an SSH session to the Local Manager through the terminal. These steps are described in the Port Forwarding section.
Port forwarding
If the FBB and BGAN terminals provide the Local Manager a private IP address, port forwarding must be performed on the terminal to allow an SSH session to terminate on the Local Manager's private IP address from the user workstation. This configuration will most likely be completed using the terminal's web interface. The Local Manager is set to accept SSH sessions on TCP port 22 by default.
- Configure the terminal to forward TCP port 22 packets to the Local Manager's private IP address.
- If possible, configure the terminal to reserve the IP address for the Local Manager MAC address.
Address redirection
The Control Center will display IP addresses reported by the Local Managers. To connect over SSH from the user's workstation Terminal Applet to a NAT(ted) IP address, the Control Center Applet must be directed to ignore the reported IP and use the terminal's routable address. This is done using System Properties to override SSH values. Below, the Local Manager is using an OOB path and circled is the private IP address as well as the IP address to use for SSH when the Local Manager is OOB.
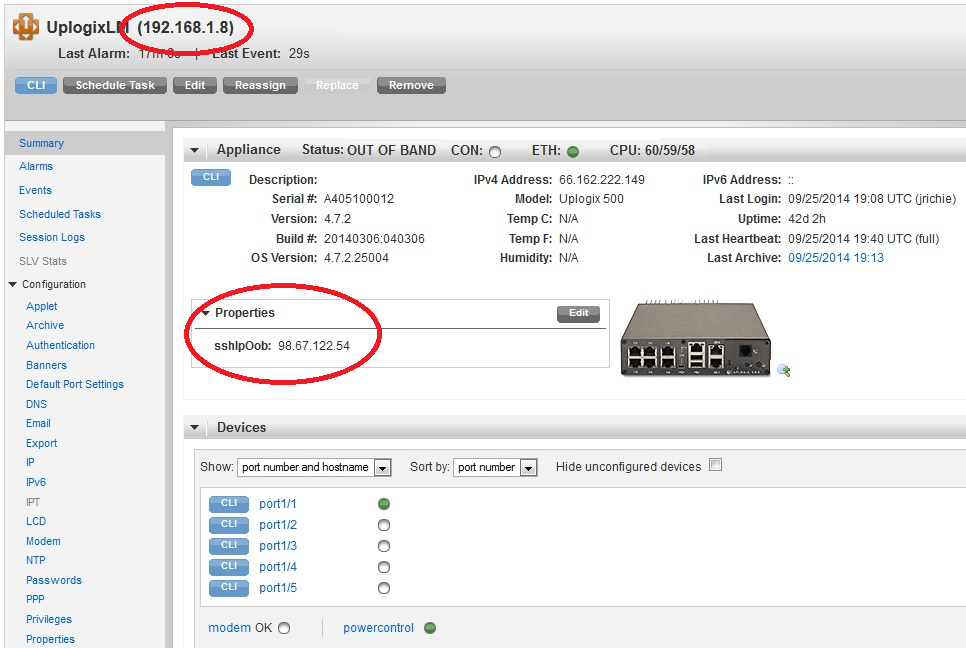
Property choices include:
- sshIP: The IPv4 address that the Terminal Applet will connect to when accessing the Local Manager from the user workstation or SOCKS proxy
- sshIP6: The IPv46address that the Terminal Applet will connect to when accessing the Local Manager from the user workstation or SOCKS proxy
- sshPort: If Port Address Translation is in use between the user workstation and the Local Manager, the configured SSH TCP port number is stored in this property
- sshIpOob: The IPv4 address that the Terminal Applet will connect to when accessing the Local Manager from the user workstation in Out of Band mode
- sshPortOob: If Port Address Translation is in use between User Workstation and Local Manager, in Out of Band mode, the configured SSH TCP port number is stored in this property
- sshIpv6Oob: The IPv6 address that the Terminal Applet will connect to when accessing the Local Manager from the User Workstation or SOCKS proxy in Out of Band mode
If the terminal's in-band WAN IP address changes (for example, if using DHCP), then you may be able to use Dynamic Domain Name Service (DDNS) from a workstation using the same routable address. In such a case you would configure the sshIpOOB override to be the qualified hostname set up with your DDNS provider.

If port address translation is used to overload the terminals routable address with more than one translation, a TCP port override property can be used as well.